An open access journal
An open access journal
Effects of Fermented non-conventional Feed on Organ Indices and Immune-Related Gene Expression in Fattening Bamei Pigs
Abstract
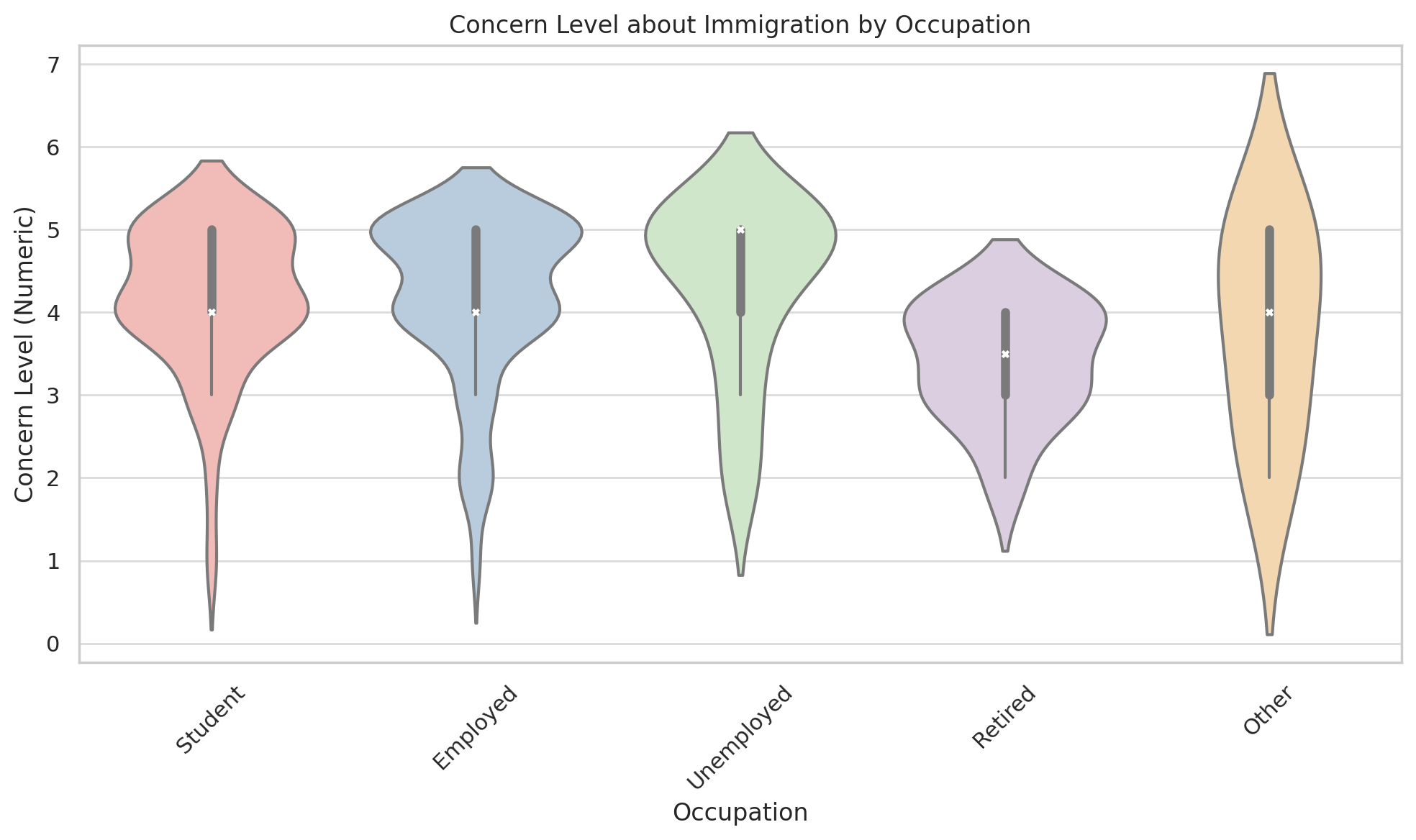
【Objective】 To investigate the effects of substituting fermented non-conventional feed for the basal diet in fattening Bamei pigs. 【Methods】Seventy-two Bamei pigs during the fatling period were randomly divided into two groups, each containing six replicates with six pigs per replicate. The control group (CK) was fed a corn-soybean meal basal diet, while the experimental group (FK) received the basal diet supplemented with 10% fermented non-conventional feed (dry matter basis) as an equal replacement. After 60 days of feeding, twelve pigs from each group were slaughtered for sample collection and performance evaluation. 【Results】 The results demonstrated that fermented non-conventional feed significantly reduced the cardiac organ index (P < 0.05) and increased the renal organ index (P < 0.05). Regarding immune-related gene expression, the feed markedly elevated the relative mRNA expression levels of IL-1, IL-2, TNF, IgA, and IgM in both lymphoid and hepatic tissues (P < 0.01). 【Conclusion】 In summary, replacing 10% of the basal diet with non-conventional fermented feed improves the health status and immune function of fattening Bamei pigs. Thus, substituting conventional feed with fermented non-conventional feed is not only feasible but also offers an economically efficient nutritional strategy for local pig breeds farming.
Share and Cite
Article Metrics
References
- SUN S, LI B, WU M, et al. Effect of dietary supplemental vitamin C and betaine on the growth performance, humoral immunity, immune organ index, and antioxidant status of broilers under heat stress. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023, 55(2): 96.
- XIONG M L (熊忙利), ZHANG W J (张文娟), ZHANG Z S (张兆顺). Effects of free-range rearing under acacia forest on blood routine, serum biochemical indexes and visceral organ indexes of rehmannia chickens (槐树林下散养对芦花鸡血常规、血清生化指标及内脏器官指数的影响). Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine (黑龙江畜牧兽医), 2019, (06): 51-53.
- DE FEO, P., LUCIDI, P. Liver protein synthesis in physiology and in disease states. Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care, 2002; 5(1), 47-50.
- TANG L (唐璐), CHAO Y Y (曹岩岩), WEI J J (蔚建军). Effects of fermented mushroom bran feed on growth performance, intestinalmicrobiota, and immune function of fattening pigs (平菇菌糠发酵饲料对育肥猪生长性能、肠道微生物和免疫功能的影响). China Feed (中国饲料), 2025, (02): 73-76.
- ROSS, S. H., CANTERLL, D. A. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annual review of immunology, 2018; 36, 411-433.
- ROJO, J. M., REJAS, M. T., Ojeda, G., et al. Enhancement of lymphocyte proliferation, interleukin-2 production and NK activity by inmunoferon (AM-3), a fungal immunomodulator: variations in normal and immunosuppressed mice. International journal of immunopharmacology, 1986, 8(6), 593-597.
- MANLAPIG, J. J. D., MATSUI, H. Production and Utilization of Fermented Rice Bran as Animal Feed. Animal science journal = Nihon chikusan Gakkaiho, 2025, 96(1), e70037.
- GHALAMKARI, G., TOGHYANI, M., TAVALAEIAN, E., et al. Efficiency of different levels of Satureja hortensis L. (Savory) in comparison with an antibiotic growth promoter on performance, carcass traits, immune responses and serum biochemical parameters in broiler chickens. African Journal of Biotechnology, 2011, 10, 13318-13323.
- GUO Y, LIU J, TUO Q, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation of Lycium barbarum leaves on the growth performance, organ indexes and intestinal microflora of rats. Frontiers in veterinary science. 2024, 11, 1416793.
- JIANG H J (蒋慧姣). Study on Application of Fermented CassavaResidues in Huanjiang Mini-pigs Production (发酵木薯渣在环江香猪养殖中的应用研究). Changsha: Hunan Agricuitural University(长沙:湖南农业大学), 2020.
- LIU X N (刘祥年), YIN X T (殷熙彤), TANG Y R (唐于然), et al. Effects of Different Proportion of Whole Plant Silage Corn on Slaughtering Performance, OrganIndex, Meat Quality and Economic Benefit of Hezuo Pigs (不同比例全株青贮玉米对合作猪屠宰性能、器官指数、肉品质和经济效益的影响). Feed Industry (饲料工业), 2025, 46(01): 64-69.
- LIU B X刘柏亨. Effect of substituting fermented rapeseed meal for soybean meal in low-protein diets on the production performance, immunity, antioxidantcapacity, intestinal health, and meat quality of finishing pigs. (发酵菜粕替代低蛋白日粮中豆粕对育肥猪生产性能、免疫力、抗氧化性能、肠道健康和肉品质的影响). Chongqing: Southwest University (重庆:西南大学), 2024.
- DELONGg C, SHARMA S. Physiology, Peripheral Vascular Resistance. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; May 1, 2023.
- LEDOUX J., GEE D M, Leblanc N. Increased peripheral resistance in heart failure: new evidence suggests an alteration in vascular smooth muscle function. British journal of pharmacology, 2003, 139(7): 1245-1248.
- SÁNCHEZ B, DELGADO S, BLANCO-MÍGUEZ A, et al. Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease. Molecular nutrition & food research, 2017, 61(1): 1600240.
- SNOECK V, GODDEERIS B, COX E. The role of enterocytes in the intestinal barrier function and antigen uptake. Microbes and Infection, 2005, 7(7): 997-1004.
- MIZUMACHI K, AOKI R, OHMORI H, et al. Effect of fermented liquid diet prepared with Lactobacillus plantarum LQ80 on the immune response in weaning pigs. Animal, 2009, 3(5): 670-676.
- WANG T, TENG K, LIU Y, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum PFM 105 Promotes Intestinal Development Through Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Weaning Piglets. Frontiers in Microbiology. 2019, 10: 90.
- WANG C, WEI S, XU B, et al. Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium co-fermented feed regulates lactating sow's performance, immune status and gut microbiota. Microb Biotechnol. 2021, 14(2): 614-627.
- CHEN J, MOU L, WANG L, et al. Mixed Bacillus subtilis and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum-fermented feed improves gut microbiota and immunity of Bamei piglet. Front Microbiol. 2024, 15: 1442373.